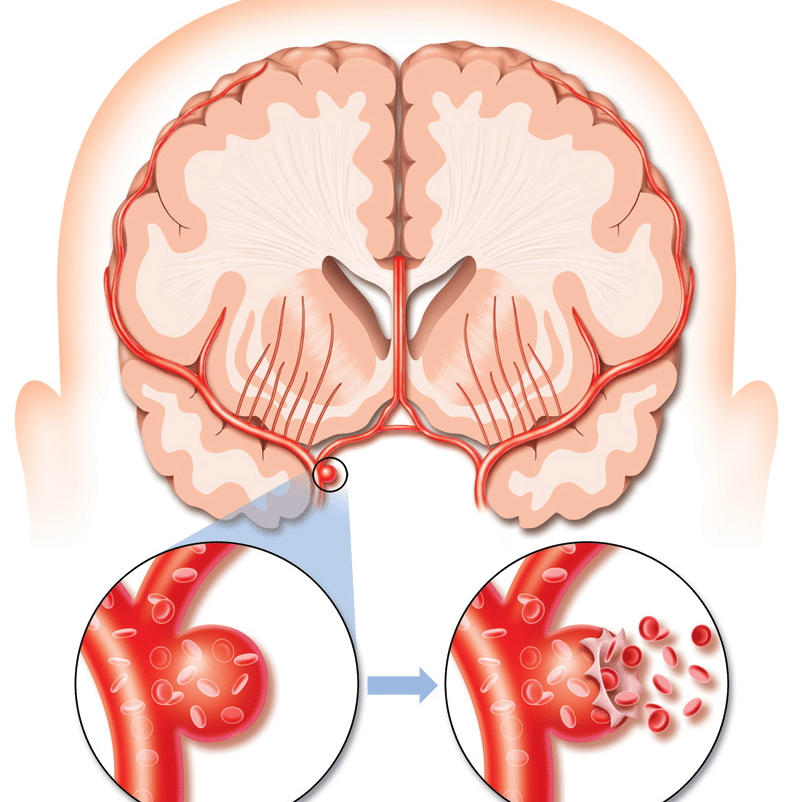
Hemorrhagic Stroke Treatment
The treatment of a hemorrhagic stroke depends upon the cause of the bleeding (e.g., head trauma, high blood pressure, vessel malformation, use of DE coagulant medications). Most patients are monitored closely in a medical care unit throughout and once a hemorrhagic stroke.
The initial care of someone with hemorrhagic includes many components:
- Determining the cause for the hemorrhagic
- Controlling the pressure
- Stopping any medication that might increase hemorrhagic. If the patient has been taking a blood thinner, specific treatments or transfusions of curdling factors is also given to prevent in-progress hemorrhagic.
- Measuring and dominant the pressure at intervals in the brain and at intervals in the skull
Pressure within the brain will be measured by inserting a tool, referred to as a ventriculostomy tube, through the skull into a locality of the brain referred to as the ventricle. If the pressure is elevated, a tiny low quantity of bodily fluid will be aloof from the ventricle. A ventriculostomy may also be wont to drain blood that has collected within the brain as a result of the stroke. The procedure will be done at the patient’s side.
Surgical treatment — A surgery is also suggested to forestall or stop hemorrhagic or scale back the pressure within the skull. Relying upon the stroke severity and therefore the patient’s condition, surgery is also done at intervals the primary forty-eight to seventy-two hours once the hemorrhage or it’s going to be delayed till one to 2 weeks later to permit the patient’s condition to stabilize.

